Abstract
Various traits differentiate entrepreneurs from non-entrepreneurs, making the former successful and the latter more likely to face failure in their ventures. Some of these traits include leadership skills, risk-taking initiatives, openness to organizational change, and perseverance in the face of challenges and failure. Two of the most accomplished entrepreneurs are Jeff Bezos, who founded Amazon, and Bill Gates, who co-founded Microsoft. These entrepreneurs have shown remarkable leadership and transformed their startups into some of the largest corporations in the world. They have achieved this feat by rallying their followers to support and implement their vision. This report has evaluated the traits and strategies used by Gates and Bezos and compared them with those used by non-entrepreneurs to develop important insights on what it takes to excel in entrepreneurship.
The report explains that successful entrepreneurs should be willing to take calculated risks, embrace strong leadership skills, practice perseverance, learn from failure, and engage in corporate social responsibility to strengthen their brands’ public image. Additionally, successful entrepreneurs should develop strong networks and create a continuous improvement and innovation culture to pivot and exploit market opportunities. However, non-entrepreneurs are known to be characterized by a fear of taking risks, weak leadership skills, impatience, lack of intense social and professional networks, and an organizational culture resistant to change.
Why Entrepreneurial Companies Outperform the Competition
Introduction
Although entrepreneurs usually face challenges in the path to success, they can generally overcome the obstacles they face and transform their startups into large companies with a comprehensive market presence. Some of the globally-renowned entrepreneurs include Bill Gates and Jeff Bezos. They have excelled in entrepreneurship and are billionaires who have grown their companies from startups into multi-billion and trillion-dollar corporations. Therefore, it is essential to evaluate their entrepreneurship strategies and personal traits that differentiate them from non-entrepreneurs to understand what it takes to succeed. This paper will provide a background on these entrepreneurs and their crucial life lessons, analyze their entrepreneurial traits, how they innovate and overcome obstacles, and how they handle failure.
Outstanding Entrepreneurs and Key Lessons in Life
One outstanding entrepreneur is Jeff Bezos, the founder and former CEO of Amazon. His company focuses on e-commerce, digital streaming, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence (Amazon, 2020). He started the business in 1994 from his garage in Washington as an online bookstore and gradually grew it into a $1.71 trillion company by 2021 (Amazon, 2021). Currently, Bezos is the world’s richest person. One of the valuable key life lessons from Bezos is applying the “regret minimization framework.” This is a concept where people picture themselves at an advanced age, try to imagine their biggest regret in life during the old period, and then work backward to take actions that will prevent remorse.
Bezos applied this framework when deciding whether to quit his former job at Wall Street and start an internet company. He realized that he would regret missing out on entrepreneurship opportunities on the internet, so he quit his job and started Amazon (Bayers, 1999). Bezos used the same framework when choosing an appropriate leadership style, and he embraced transformative leadership, where leaders work with teams to create a vision and implement change (Fridson, 2001). Bezo’s actions show that successful entrepreneurs should not only embrace risk and follow their vision but they should also use leadership to inspire followers to adopt change.

Exhibit 1: Amazon’s Revenues
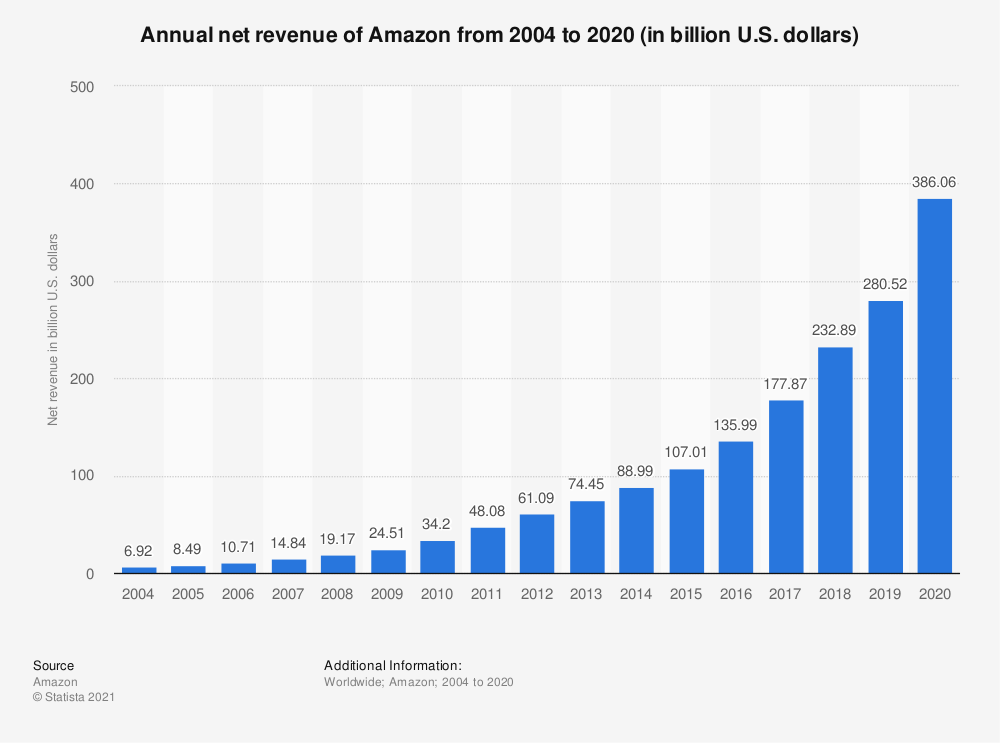
Source: https://www.statista.com/statistics/266282/annual-net-revenue-of-amazoncom/
The second entrepreneur is Bill Gates, the co-founder of Microsoft Company, which develops and manufactures computer electronics, computer software, personal computers, and other technology products. Gates and his co-founder (late childhood friend) Paul Allen invented the first product, the rudimentary computer, in 1972. Since then, he has provided leadership at Microsoft as CEO, and the company’s value surpassed the trillion-dollar mark and is currently worth in excess of $2 trillion. (See Exhibit 2). One of Gates’s most important life lessons is the importance of continuous innovation by taking risks and thinking ahead of time.
Gates had a vision of becoming the most successful software company. Despite intense competition from established firms such as IBM, he ventured into the competitive software industry when he released the software product Xenix in 1980 (Microsoft, 2020). He took a fundamental risk by dropping out of Harvard to create Microsoft Company in 2008 (Fridson, 2001). This demonstrates that successful entrepreneurs have a solid vision and are persistent in achieving that vision regardless of their circumstances or obstacles. Gates applies both autocratic and transformational leadership, required in the rapidly changing tech world where accurate decisions need to be made promptly.

Exhibit 2: Microsoft Revenues
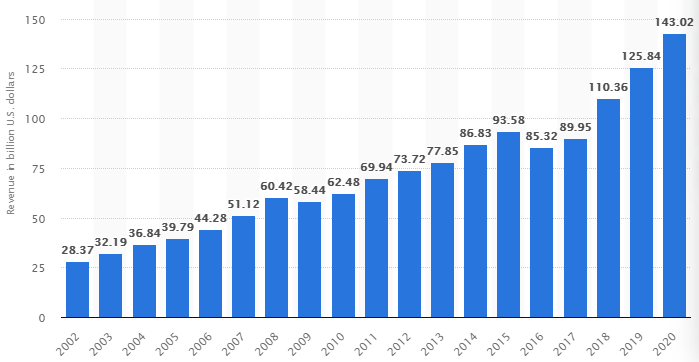
Source: https://www.statista.com/statistics/267805/microsofts-global-revenue-since-2002/
Traits Entrepreneurs Share Which Make Them Perform Better than Non-Entrepreneurs
Taking Risks
Entrepreneurs often take risks in their quest to pursue and achieve their vision. They tend to act quickly and decisively to make the most of the opportunities that they have identified. For example, Gates and Bezos took risks by leaving education and employment opportunities in prominent organizations to pursue their vision. When entrepreneurs take such significant risks, they are likely to work hard and remain focused on their image since failure is no longer an option. For example, Bezos knew that he had to make Amazon successful since he quit a lucrative job opportunity on Wall Street. He had to remain focused to achieve his vision and not have regrets in life at an old age (Bayers, 1999).
Persistence and Perseverance
Many entrepreneurs embody these two traits: aggressively work hard to pursue a vision and overcome obstacles they face in their path. Gladwell (2008), in the book Outliers, discusses the concept of the 10,000-hour rule, which states that people should perform deliberate practice for 10,000 hours before they can become world-class in a field. This entails pushing one’s skill as much as a person can in the quest to excel in a specific area. Gates, Bezos and Plank, have all accomplished the 10000-hour rule, which is a manifestation of their persistence and perseverance in pursuing their visions (Kouzes & Posner, 2007). Persistence and determination are closely related to handling failure, and many entrepreneurs who face loss will learn from it and improve their future outcomes.
Strong Leadership Skills
One of the most common traits associated with successful entrepreneurs is strong leadership. All entrepreneurs require strong leadership skills to rally their followers towards a shared vision and goal (Gladwell, 2008). Many successful entrepreneurs such as Jeff Bezos apply transformative leadership to build solid teams and use charismatic traits to inspire them to embrace transformative change. Bill Gates has been known to use the autocratic leadership style when making important, sensitive, and time-barred decisions. Ventures owned by non-entrepreneurs stagnate in terms of innovation, and they are unable to respond to the constantly changing needs of customers. Ultimately with this type of organizational behavior, such ventures fail.
Corporate Social Responsibility
Finally, many successful entrepreneurs implement corporate social responsibility (CSR). For example, Bill Gates created the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, the largest private foundation globally (Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, 2020). It invests in health, social welfare, and education (See Exhibit 3). Bezos also contributes to charity, and for example, he made a $10 million donation to Seattle’s Museum of History and Industry in 2011 (Market Realism, 2020). Corporate social responsibility creates a positive public image of entrepreneurs’ companies and attracts consumers to a brand.
Exhibit 3: Bill and Melinda Gates Donations past 20 years
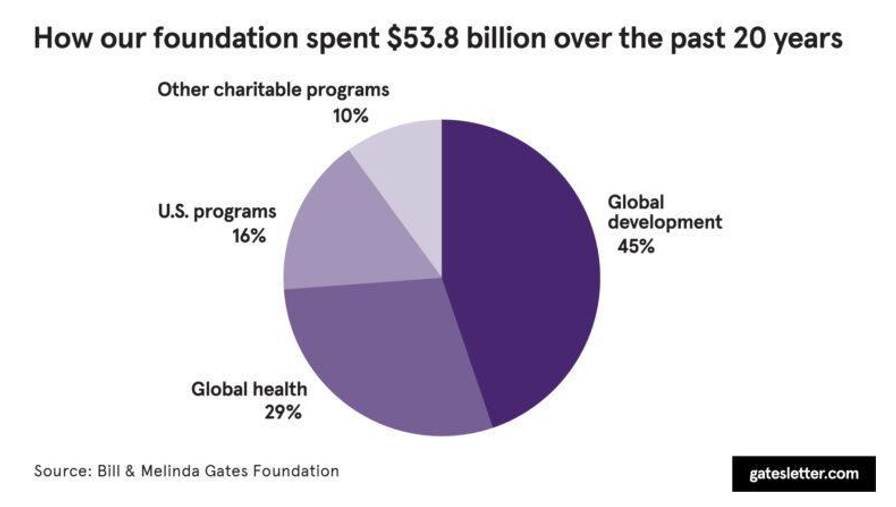
Source: https://www.gatesnotes.com/2020-Annual-Letter
How Entrepreneurs Pivot as Compared to Non-Entrepreneurs
Creating a Culture of Continuous Innovation and Improvement
Entrepreneurs usually pivot by creating a culture of continuous innovation and improvement within the company. Constant innovation ensures that a venture takes advantage of any market opportunities to improve the existing products, launch new products or target new market segments. Most successful entrepreneurs usually invest heavily in research and development to identify existing market opportunities and diversify their product portfolio. For example, Bezos has created a culture of continuous innovation at Amazon and has grown its brand portfolio to over 75.1 million products sold on Amazon as of March 2021. (See Exhibit 4). However, non-entrepreneurs usually fail to create a culture of continuous improvement, generally due to a lack of strong leadership. As previously discussed, weak leaders are unable to inspire followers to adopt change initiatives that create value. An example is Kodak Company, which failed to embrace digital photography opportunities since its culture was not receptive to change and continuous improvements, which led to its collapse (Buchia, 2015).
Exhibit 4: Estimate of the number of products currently selling on the Amazon US website:
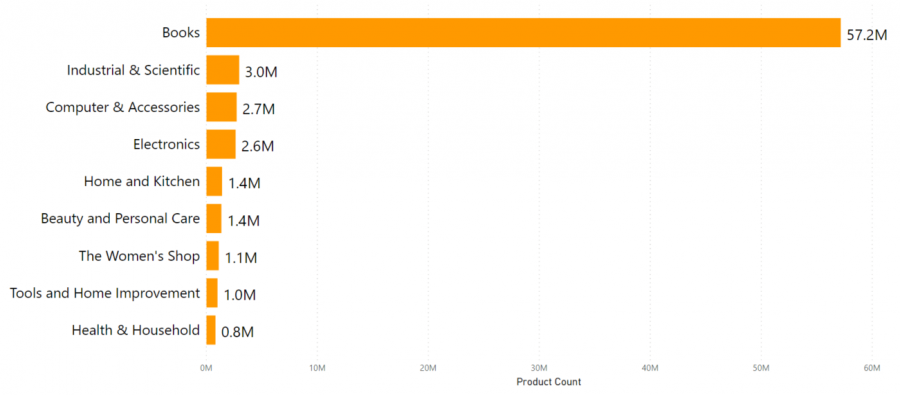
Source: https://www.scrapehero.com/how-many-products-does-amazon-sell-march-2021/
Networking
“However, he viewed failure as an opportunity to learn from mistakes, and he implemented improvements when innovating new products in the future. (Haralambous, 2018).” Entrepreneurs recognize the importance of social and professional networks in enabling them to understand and exploit market opportunities
Many successful entrepreneurs surround themselves with people who complement their areas of weakness and better understand the industry they operate in. Moreover, one of Bill Gates’ well-known quotes is, “Surround yourself with people who challenge you, teach you and push you to be your best” (Buchia, 2015).
How Entrepreneurs Handle Failure
Entrepreneurs usually understand that they will experience failure at certain points in life and create an opportunity to better themselves for future initiatives. Entrepreneurs do not give up when faced with failure. Instead, they seek lessons that will help them achieve a better outcome in the future. Jeff Bezos has faced failure several times, and many products introduced to Amazon fail to be successful.
Conclusion
This report evaluates and highlights the strong traits of successful entrepreneurs such as Jeff Bezos and Bill Gates. Some of the main factors that differentiate entrepreneurs from non-entrepreneurs are their ability to exercise strong leadership, take risks, create a continuous improvement culture, invest in networking opportunities, and handle failure well. These leaders could transform their vision into reality, and they grew their startups into multi-billion and trillion-dollar corporations.